Medical researchers are discovering how our internal clock affects disease. They found a link between our sleep cycles and cancer risk. This is a big deal in modern medicine.
Your body’s timing system does more than make you sleepy at night. Scientists know now that messing with it can harm your health. People who work odd hours, travel a lot, or sleep irregularly face more cancer risks.
Studies show timing affects cell repair and immune function. Researchers are creating new treatments that work with your body’s rhythms. This is a big step forward.
This new area of study brings hope for better prevention and treatments. We’ll look at the latest research that’s changing how doctors treat cancer. It’s all about working with your body’s natural schedule.
Understanding Circadian Rhythm and Its Importance
Deep in your brain, a biological clock controls your daily rhythms with great precision. It affects your alertness and immune system’s ability to fight diseases. Knowing about these cycles helps you make better health choices and see why timing is key for your wellbeing.
What is Circadian Rhythm?
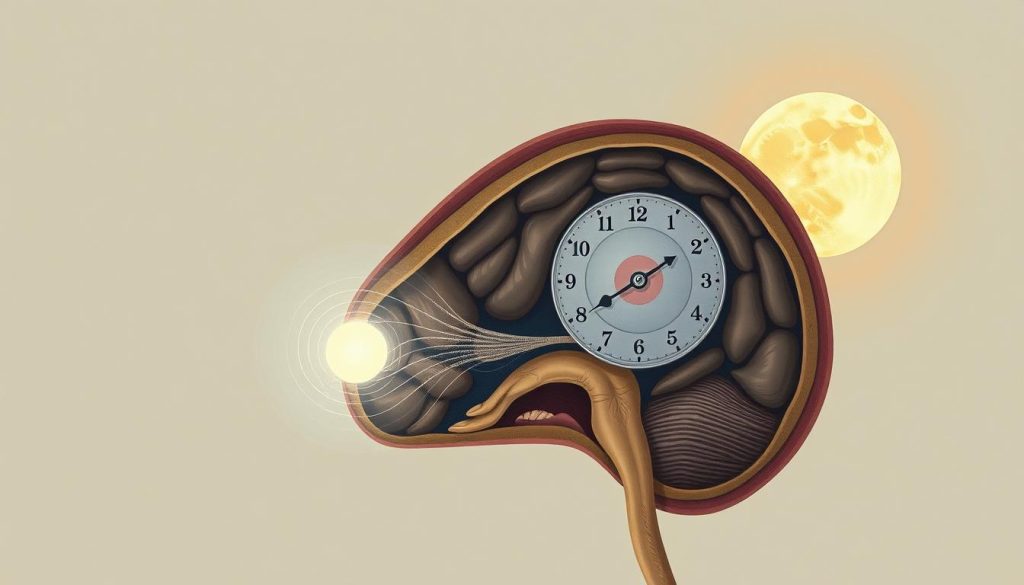
Your circadian rhythm is like a master clock in your brain. It’s in a small area called the suprachiasmatic nucleus. This tiny control center manages a 24-hour cycle that affects every cell in your body.
This clock responds to light and darkness. When light hits your eyes, it sends messages to your brain about the time. Your body then adjusts hormone production and body temperature.
Circadian rhythms have evolved over millions of years. Your ancestors needed to be alert during the day and rest at night. This ancient programming still guides your biology today, even with modern lifestyles.
How Circadian Rhythms Affect Sleep
Your sleep patterns are controlled by circadian rhythm signals. These signals regulate melatonin levels, making you feel sleepy at night. This usually starts around 9 PM for most people.
When your circadian rhythm works right, you sleep and wake up naturally. But sleep disruption can cause health problems.
Many things can disrupt your sleep rhythms:
- Exposure to bright screens before bedtime
- Irregular sleep schedules
- Shift work or frequent travel across time zones
- Caffeine consumption late in the day
- Artificial lighting during evening hours
The Role of Circadian Rhythms in Health
Your circadian rhythm does more than control sleep. It regulates many biological processes that keep you healthy. For example, your immune system follows daily patterns to fight infections.
Hormone production also follows circadian patterns. Cortisol levels peak in the morning to wake you up. Growth hormone is released during deep sleep. Even your liver processes toxins better at certain times.
Regular sleep disruption can lead to serious health issues. Research links chronic circadian rhythm problems to increased risks of:
- Cardiovascular disease and high blood pressure
- Diabetes and metabolic disorders
- Weakened immune system function
- Mental health issues like depression and anxiety
- Certain types of cancer
Your body temperature, blood pressure, and even medication effectiveness vary with circadian timing. Doctors now consider chronotherapy to match treatments with your body’s rhythms. Understanding these patterns helps you work with your biology.
The link between circadian health and wellbeing is strong. Disrupting these rhythms can affect your body’s DNA repair and cellular health. This makes regular sleep patterns crucial for long-term health.
The Link Between Circadian Rhythm and Cancer
Our body’s internal clock is key in fighting cancer. It controls when cells repair, divide, and get rid of damaged parts. This is more than just about sleep.
When our internal clock works right, it helps keep our cells healthy. It does this by managing when genes are active. This ensures our body’s defenses against cancer are at their strongest.

How Disruption Affects Cancer Risk
When our internal clock is off, cancer cells can grow. This is because our body’s protective systems start to fail. This failure hits our cells’ ability to fix DNA damage hard.
Our cells usually fix DNA damage during specific hours. But when our clock is off, this work gets delayed. This means damaged DNA stays unrepaired for longer.
Our body’s ability to stop tumors also gets weaker. Genes like p53 and BRCA1 work best at certain times. But when their timing is off, they can’t stop cancer cells as well.
Night shift workers are at higher risk of cancer. Studies show they get more breast, prostate, colorectal, and lung cancer.
Key Studies Supporting the Connection
Harvard Medical School found that changing our internal clock affects gene activity. They saw that even small changes can let cancer cells grow more easily.
A big study in the Journal of Clinical Investigation followed 75,000 nurses for 22 years. It found that women working night shifts for over 15 years had twice the risk of breast cancer. This study showed a clear link between night work and cancer.
Research from the University of Pennsylvania showed that a disrupted clock weakens our immune system. This system is key in finding and killing cancer cells. But when our clock is off, it can’t do its job as well.
Studies from top cancer centers found that genes that fight cancer have daily schedules. When these schedules are messed up, these genes can’t protect us as well. This research is helping us understand how to prevent and treat cancer better.
Current Research on Circadian Rhythms and Cancer
Recent studies are changing how we fight cancer. Scientists found that cancer cells have messed-up clocks. This messes with how tumors grow and react to treatments.
Teams at top research places are finding new ways to use this info. They’re creating better treatment plans based on timing. These plans are showing great promise for better patient results.
Notable Recent Findings
Researchers at MD Anderson Cancer Center found special biomarkers for treatment success. These biomarkers include proteins like CLOCK and BMAL1. They can check these proteins in tumor tissue and blood.
They found links between cell cycles and circadian rhythms. Cancer cells without a rhythm control grow fast but can be weak to treatments.

Studies at the Salk Institute show biomarkers can tell how aggressive cancer is. They also help find the best treatment time for each patient. This is a big step forward in cancer care.
Healthy cell cycles need good circadian rhythms. When this fails, cancer cells grow out of control. Knowing this opens up new ways to treat cancer.
Promising Clinical Trials
Clinical trials are testing timing-based treatments in many places. The University of Pennsylvania is leading studies on the best treatment times. Patients get chemotherapy and radiation when their body’s clock is right.
Early results show big improvements in treatment success. Some trials see up to 40% better results when treatments match natural rhythms. Patients also have fewer side effects.
These trials use biomarkers to find the best treatment times. Researchers check circadian proteins to guess when patients will respond best. This precise medicine is changing cancer treatment.
The studies also look at how cell cycles affect treatment success. Cancer cells are most weak during certain circadian times. Timing treatments for these moments makes them more effective while protecting healthy cells.
Strategies to Maintain a Healthy Circadian Rhythm
Keeping your circadian rhythm in check is crucial for fighting cancer. Studies show that those with regular daily routines have lower cancer rates. Your body’s internal clock responds to light, meals, exercise, and social signals.
Your circadian system needs these signals to stay in sync. When they work together, they protect against cell damage and tumor growth. Even small changes in your routine can boost this natural defense.

Sleep Environment Optimization
Start by controlling light in your bedroom. Use blackout curtains or eye masks to block out light. Keep your bedroom cool, between 65-68°F, for better sleep.
Turn off electronic devices an hour before bed. The blue light from screens can lower melatonin levels. This hormone is key for sleep and cancer prevention.
Stick to a consistent sleep schedule, even on weekends. Going to bed and waking up at the same time every day helps keep your rhythm strong. This is especially important for those with shift work.
Timing Your Daily Activities
When you eat affects your circadian rhythm and cancer risk. Eat your biggest meal in the morning for better metabolism. Eating late at night can disrupt sleep and repair processes.
Get morning light to reset your clock. Spend 15-30 minutes outside in the morning. This natural light helps your body start the day’s repair and hormone production.
Exercise at the same time each day to strengthen your rhythm. Morning or afternoon workouts are best. Evening exercise can make it hard to sleep.
For those with shift work, light therapy can help. Use bright light during work hours and darkness at night. This helps keep your rhythm stable, no matter the time.
Chronotherapy is a new field that helps plan your day for cancer prevention. It looks at the best times for medication, meals, and exercise based on your rhythm.
Melatonin supplements can help with sleep, but only under a doctor’s guidance. Timing and dosage are very important for safety and effectiveness.
Future Directions in Circadian Rhythm and Cancer Studies
The field of circadian rhythm and cancer research is at an exciting point. Scientists are working on new technologies. These could change how we prevent and treat cancer in the future.
Emerging Technologies in Research
Advanced wearable devices now track our circadian biomarkers in real-time. These smart monitors help researchers understand our rhythm patterns better than ever. Artificial intelligence systems analyze huge datasets to find connections between sleep and cancer.
Gene therapy is showing promise for fixing cellular rhythms. Scientists are looking into ways to make cancer cells follow normal rhythms. This could help cells repair DNA and die naturally when needed.
Potential for New Treatment Approaches
Chronotherapy is the most promising area in cancer treatment timing. Doctors are learning to schedule medications at the best times for our body rhythms. This could make treatments more effective and reduce side effects.
Light therapy devices are getting more advanced and personalized. Soon, patients might get light prescriptions to keep their sleep patterns healthy during treatment. Combining chronotherapy with immunotherapy could also boost our immune system’s fight against cancer.
These advances bring hope for better cancer care that works with our bodies. The future of cancer treatment may rely on understanding the simple rhythm of day and night.

