The blue spectrum has been shown to have strong positive benefits for human health. For this reason, blue light is often used in the treatment of certain medical disorders, such as cataracts, macular degeneration, age-related macular degeneration, and rheumatoid arthritis. It is also used to treat depression, migraines, high blood pressure, anxiety, and to stimulate the immune system. The specific wavelength of blue light (circadian blue) that has to be regulated to promote good health and circadian rhythm is 439-492nm. The lowest threshold levels of blue light required to achieve effective day-time lighting (Sunset to sunrise) is 20 W/cm2.
Blue Light Photoreceptor – Important Gene For Circadian Rhythm
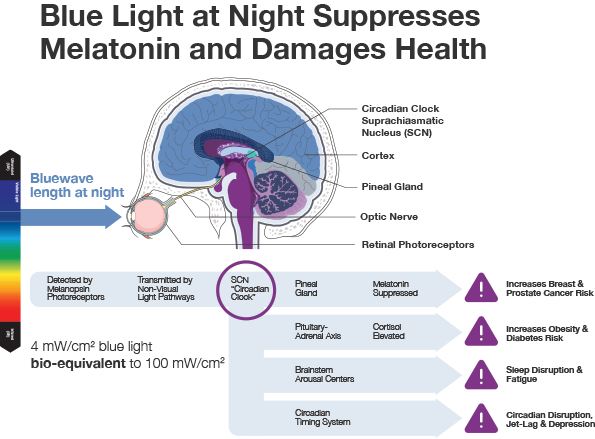
To understand how blue light and melatonin affect your body clock, it is important to know how light and darkness affect the human circadian rhythm. Human circadian rhythm is a complex network of genes that control the timing of our biological clocks which are closely associated with the sleep-wake and food-draining cycles. It helps us understand how blue light can affect the biological clock of our bodies.
Basically, light and darkness are the main drivers of our internal biological clocks. These clocks are made of small protein structures called ‘cryptochromes’ or in simpler terms, light-sensitive cells (photo-sensory neurons). Each cell in our body has a set of doublets of DNA (genetic instructions) programmed into it and these doublets are coupled together in a highly complicated series of interactions. Every day, the DNA binding to each cryptochrome is switched on and off making the whole process of genetic instruction run like clockwork.
The circadian rhythm is set to be synchronized 24 hours per day by the proteins, N-type calcium channels in the retinohypothalamic tract. However, this system is activated by the light at different times of the day. Most significantly, melatonin and other proteolytic enzymes that generate the biological response in the cryptochromes are produced during the night as a result of a disruption in the darkness. The irregularities caused by the disruption of the circadian rhythm are called ‘disruption’ and they have an impact on the protein levels and their stability in the human body.
The ability of the cells to make and release melatonin is compromised in the presence of light. The disruption of the circadian rhythm by light can cause a disruption of the sleep-wake patterns of the animal. When the animal is sleeping, the cryptochromes play a crucial role in the generation of the proteins that regulate the biological clock. In the case of humans, the dysfunctional or abnormal function of cryptochrome can cause serious medical conditions, including sleep disorders, psychiatric disorders, and certain types of cancer. As a consequence of the dysfunctional protein structure, the quality of sleep is altered.
The circadian light/cry protein interaction has a profound effect on the transcription of various genes in the animal body. This process regulates the genes that control the strength and duration of the regeneration of the cells. Some of these genes include the genes that are involved in the development of the neuroendocrine system and those that control the behavior of the central nervous system. The regulation of these genes is highly influenced by the effects of the disrupting light/cry protein interactions. The researchers showed that the enrichment of the transcripts of the genes that control neuroendocrine system processes was highly affected by the disrupting light/cry protein interactions.
Blue Light Sleep Aid
The researchers were able to identify the causal relationship between the blue light and its effect on the circadian rhythms of the drowsiness-active S. cerevisiae cells. They identified the specific set of amino acids, flavonoids and non-flavonoids called rhodopsin, which is essential for the development of the nervous system and circadian rhythms. These compounds can be found in the membranes of the photoreceptor cells in the retina of the S. cerevisiae. The study was published in the Journal of Biological Chemistry.
The circadian proteins identified in this study are unique to different species. Therefore, the researchers were able to determine the nature of the signaling pathway that was targeted by the disruption of the blue light photoreceptor in the S. cerevisiae and the effect it had on the expression levels of the transcripts of the genes controlling circadian rhythms. It is well known that the photoreceptor cells of the eye have a very complex architecture. The complex architecture of the photoreceptor cells synchronizes with the circadian rhythms in the body. The study has provided insights into how the disruption of the blue light photoreceptor can affect the expression of important genes that are involved in the development of the nervous system and circadian rhythms.
Blue Light Makes Me Sleepy – How to Get the Best Benefits
Blue light has long been recognized for its positive effects upon the human body, especially when it comes to healthy sleep. In fact, many studies have been conducted on the subject, with the results showing that exposure to blue light does improve quality sleep. The wavelength of blue light is similar to the sun’s rays, so it is most effective when it is viewed from an angle and at a proper height. Another option is to wear blue-blocking sunglasses, although these are not recommended for children under age six because they may alter their sleeping pattern. The recommended option is to wear blue-blocking window blinds or other light-blocking gear to help keep your room darkened when you are trying to get to sleep.

Studies have shown that blue light exposure during the natural circadian rhythms of human beings has a profound effect on sleep. Exposure to blue light seems to act in a manner similar to mild jet lag, wherein the body adjusts to the new time zone by slowing down its circadian rhythms. It can take about one week for the body to go back to its original rhythm, after which it usually requires more time for the adjustment to be permanent. Studies have also shown that blue light exposure at night may promote cell division and growth, which are a factor responsible for the creation of new cells and tissues in our bodies.
However, blue light has its own drawbacks, as any exposure to blue light increases the risk of photo-aging as well as increases the risk of developing certain diseases such as cancer. For this reason, it is suggested that people with chronic diseases should avoid blue light at all costs. The use of golden-colored filter sunglasses while driving should also be avoided due to the increased risk of glare and cataracts. Also, golden filter sunglasses or other light-filtering gear should be used with an eye exam regularly. As golden light has been recognized as beneficial in several areas of human biology, it has been incorporated into modern devices such as computer screens and digital camera lenses.
No Red Lights On At Night
If you’re trying to get to sleep at the end of the day, you may be tossing and turning when you look at your watch, thinking it’s time for another red light cycle. What’s red light, and is it really going to help you fall asleep in the evening? Red light is known to keep most people awake at night, which is why many experts recommend turning the lights off well before you go to bed. People don’t typically stay awake because they’re afraid they’ll have to deal with traffic the next morning. Red light simply keeps people awake for a different reason: tiredness. If you find yourself tossing and turning or having trouble staying asleep after a red light cycle, you need to make an appointment with your doctor.
There are red light bulbs out there that may help you get better sleep at night, but there’s no guarantee you won’t still be tossing and turning the next morning. Some people even think it’s more of an addiction than a good night’s sleep, but if you need to have red lights eliminated from your life, then you should definitely make an appointment with your doctor. You might have a condition that needs red light therapy instead of better sleep. In that case, you can’t afford to waste time or money on treatments that won’t work.
The red light bulb myth could be dangerous, especially if you have sleep inertia. Most people that suffer from sleep inertia don’t even realize they have the problem until their doctor tells them. If you do get red light therapy, be sure to see a doctor right away so you can be safe rather than sorry.